Disease & Illness
Is Heel Pain a Sign of Cancer? Understanding the Causes and When to Seek Medical Advice
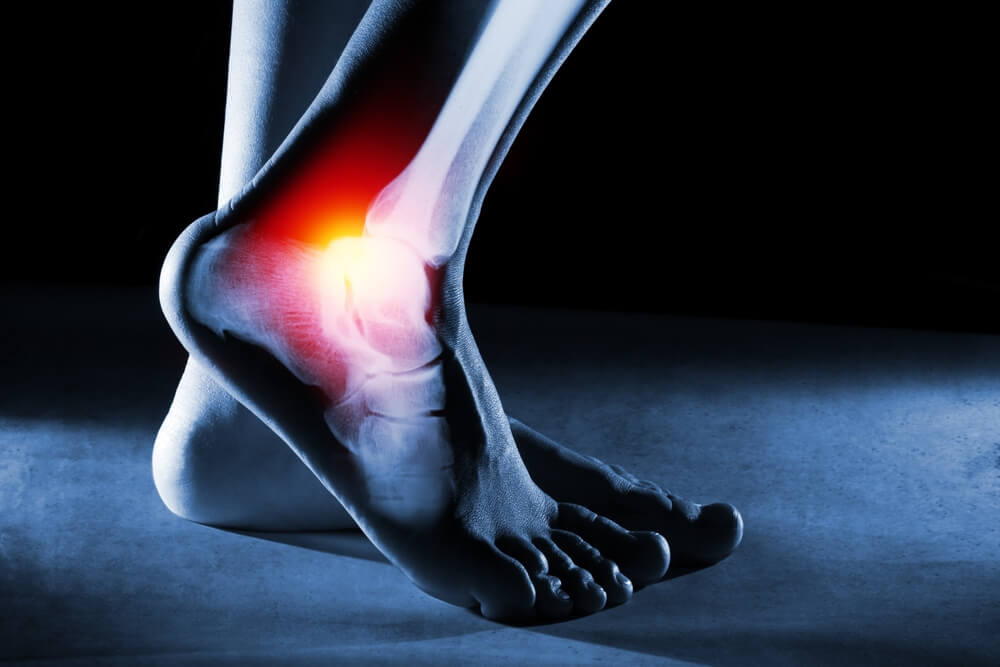
Heel pain is a common complaint that can affect anyone, from athletes to those with more sedentary lifestyles. Understanding the underlying causes of heel pain is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. One of the most prevalent causes is plantar fasciitis, a condition where the band of tissue running across the bottom of your foot becomes inflamed, often due to overuse or improper footwear. Another frequent culprit is heel spurs, which are calcium deposits that form on the underside of the heel bone and can cause significant discomfort.
Achilles tendonitis is another common reason for heel pain. This condition occurs when the Achilles tendon, which connects your calf muscles to your heel bone, becomes irritated or inflamed due to repetitive stress or sudden increases in activity levels.
While these are some typical causes, it’s important not to overlook other potential reasons for heel pain. In rare cases, persistent heel discomfort could be a sign of more serious conditions such as cancer. However, this is uncommon and usually accompanied by other symptoms.
Understanding these common foot pain reasons can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and take preventive measures to maintain foot health and alleviate discomfort effectively.
Could Heel Pain Indicate Something More Serious Like Cancer?
Heel pain is a common ailment that many people experience, often attributed to conditions like plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendonitis. However, in rare cases, persistent heel pain could be an indicator of something more serious, such as cancer. Understanding the potential link between heel pain and cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment.
While it is uncommon, certain types of cancer can manifest symptoms that include heel pain. Bone cancer signs, particularly in the foot or heel area, might initially present as persistent and unexplained discomfort. Metastatic cancer indicators can also include bone-related symptoms if the cancer has spread from another part of the body to the bones.
It’s important to recognize that not all heel pain is related to cancer; most cases are due to less severe conditions. However, if you experience chronic heel pain accompanied by other cancer symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or swelling in other areas of your body, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
While rare causes of heel pain like bone or metastatic cancers exist, they are not common. Remaining informed about these possibilities ensures timely medical advice and intervention if needed. Always prioritize your health by seeking professional guidance when experiencing unusual or persistent symptoms.
Understanding the Different Types of Cancers That Might Cause Heel Pain
Heel pain is a common issue that can arise from various causes, including certain types of cancer. Understanding the potential link between heel pain and cancer can be crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. While not all heel pain is indicative of a serious condition, it’s important to be aware of the cancers that could potentially cause such discomfort.
One type of cancer that might lead to heel pain is osteosarcoma, a form of bone cancer. Although osteosarcoma primarily affects long bones in the body, it can also occur in the bones of the foot. Osteosarcoma symptoms may include localized pain and swelling, which could manifest as persistent heel pain.
Another possibility is metastatic bone disease in the foot, where cancer from another part of the body spreads to bones in the foot. This type of metastatic spread can lead to significant discomfort and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional if suspected.
There are also rare cancers affecting feet that involve both bones and soft tissues. These include various sarcomas (cancers originating from connective tissues) that might affect areas around or within the heel. Given their rarity, these cancers require specialized diagnostic approaches to identify their presence accurately.
If you experience unexplained or persistent heel pain alongside other symptoms like swelling or changes in skin texture around your foot, consulting with a healthcare provider for further evaluation is advisable. Early detection remains key in managing any potential underlying conditions effectively.
When Should You Consult a Doctor About Your Heel Pain?
Heel pain can be a common issue, often resulting from overuse or minor injuries. However, there are certain instances where consulting a doctor becomes crucial to ensure proper treatment and recovery. Understanding when to seek medical advice is essential for addressing potentially serious foot issues.
Persistent heel pain that does not improve with home remedies such as rest, ice application, or over-the-counter pain relievers should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. If the discomfort persists for more than a few weeks or worsens over time, it may indicate an underlying condition that requires medical attention.
Be mindful of worrisome foot symptoms accompanying your heel pain. These include severe swelling, redness, warmth in the affected area, or the inability to bear weight on your foot. Such signs could suggest an infection or a more serious injury like a fracture.
Another important consideration is if you experience heel pain alongside numbness or tingling sensations in your feet. These symptoms might point to nerve-related issues that necessitate prompt evaluation by a doctor.
While occasional heel pain can often be managed at home, persistent discomfort and specific worrisome symptoms should not be overlooked. Seeking medical consultation for foot issues ensures timely diagnosis and treatment, helping you get back on your feet without unnecessary delay.
How Doctors Determine the Cause of Your Heel Pain
Heel pain can be a frustrating and debilitating issue, often requiring a thorough diagnostic process to pinpoint the underlying cause. Understanding the steps involved in diagnosing heel pain can help patients navigate their treatment journey with confidence.
The first step in diagnosing heel pain typically involves a detailed medical history and physical examination. Doctors will ask about the onset of your symptoms, any recent injuries, and your daily activities. This information helps narrow down potential causes and guides further investigation.
Once an initial assessment is complete, doctors may recommend medical tests for heel discomfort to gain more insights. Imaging for foot issues is commonly used to visualize internal structures. X-rays are often the first choice as they can reveal bone spurs or fractures that might be contributing to pain. In some cases, more advanced imaging techniques like MRI or ultrasound may be necessary to assess soft tissue conditions such as plantar fasciitis or tendonitis.
In addition to imaging, blood tests related to heel pain might be conducted if there’s suspicion of systemic conditions like arthritis or infection that could affect the heels. These tests help rule out other medical conditions that could manifest as heel discomfort.
By following these diagnostic steps, healthcare providers can develop a comprehensive understanding of your condition and tailor a treatment plan that addresses the root cause of your heel pain effectively.
Treatment Options Available if Cancer is Detected as a Cause of Heel Pain
When heel pain persists and is eventually linked to cancer, understanding the available treatment options becomes crucial. Cancer treatment options for foot involvement are diverse and depend on the specific type and stage of cancer detected. Oncological care for bone cancer in the feet region often begins with a thorough evaluation by a team of specialists, including oncologists, orthopedic surgeons, and radiologists.
Surgery is typically a primary option when dealing with bone cancer in the foot area. The goal is to remove the tumor while preserving as much function as possible. In some cases, limb-sparing surgery may be feasible, which involves removing only part of the bone affected by cancer and replacing it with a prosthesis or graft.
Radiation therapy can be employed either before surgery to shrink tumors or after to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. It is particularly useful when surgical removal is not entirely possible due to location constraints or other health considerations.
Chemotherapy might also be recommended depending on the type of cancer involved. This systemic treatment helps target any potential spread beyond the primary site in the foot region.
Targeted therapies and immunotherapies represent newer avenues in oncological care that focus on specific genetic markers or boost the body’s immune response against cancer cells.
Each patient’s treatment plan will be tailored based on individual needs, ensuring comprehensive care that addresses both medical requirements and quality of life considerations. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor recovery progress and manage any side effects effectively.
Key Takeaways on Managing Heel Pain and Ensuring Early Detection of Serious Conditions
In conclusion, managing heel pain effectively requires a proactive approach that emphasizes both prevention and early detection of potential underlying conditions. Understanding the common causes of heel pain, such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinitis, and stress fractures, is essential for implementing appropriate self-care measures. These may include rest, ice application, stretching exercises, and the use of supportive footwear designed to alleviate strain on the foot.
Moreover, recognizing when heel pain could be indicative of more serious health issues is crucial. Persistent or worsening symptoms should prompt consultation with a healthcare professional to rule out conditions like nerve entrapment or systemic diseases that may manifest as foot discomfort.
Regular monitoring and maintaining open communication with medical experts ensure that any significant changes in symptoms are addressed promptly. By prioritizing early intervention and adopting preventive strategies tailored to individual needs, individuals can effectively manage heel pain while safeguarding their overall foot health.